GROUND-SOURCE HEAT PUMP
A ground-source heat pump is a heating device that extracts heat from the environment - in this case, from the ground. Inside the pump, the heat is transformed and then supplied to the building for heating or domestic water preparation. A heating system based on this solution comprises two sources - the lower source, where the heat is extracted, and the upper source, which releases heat to the building. The pump allows the extracted heat to flow between these two sources. The pump can use different lower sources. The choice depends mainly on the conditions of the plot - its size, the type of soil, the acceptable size of the earthworks, etc. [1].
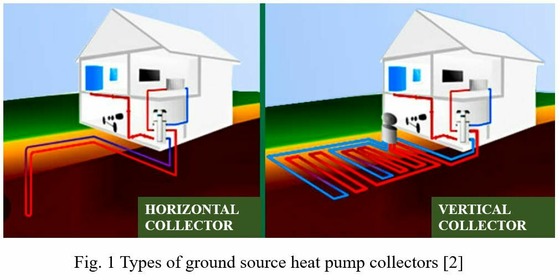
In single-family homes, the following systems are distinguished:
- A horizontal ground collector is a buried coil of pipes filled with antifreeze liquid, which is an ethyl or propylene glycol solution. This fluid circulates in the pipes and picks up heat from the ground and then, through a heat exchanger, transfers it to the pump. The cooled fluid then returns to the coils, warms up again at the expense of the ground and the cycle repeats itself.
- Vertical collectors are also pipes filled with antifreeze liquid placed in vertical, deep boreholes.