Electrochemical Storage Accumulators
Accumulator
- Accumulator (energy) - an apparatus for storing energy or power
- Different types with different materials
- Voltage of the battery cell is determined by the materials
- Capacity and current depends on the size
- For higher voltages, series circuits are required (Ex. classic car battery with 6 x 2V secondary cells = 12 V)
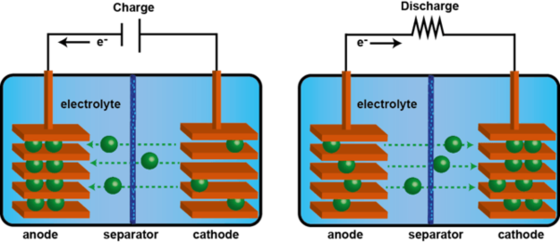
How does a battery works?
- Galvanic cell - electrochemical cell that generates electricity from movements of electrons from one element to another
- Changes in the oxidation numbers (indicator of the loss of electrons in a chemical compound)
- Oxidation (loses electrons) and Reduction (gains electrons)
- The ion or molecule that accepts electrons is called the oxidizing agent (by accepting electrons it causes the oxidation of the other)
- What donates electrons is called the reducing agent